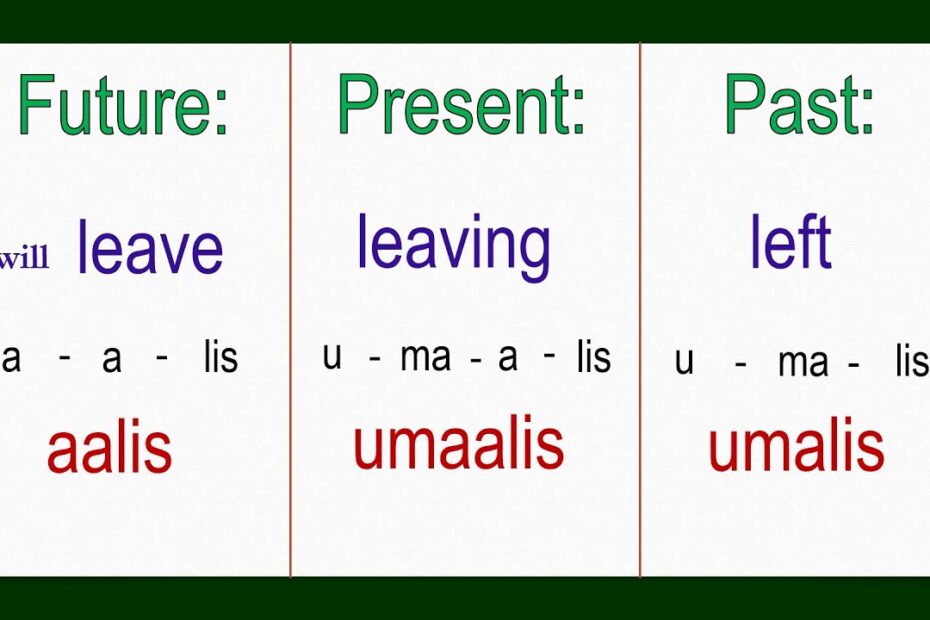
Understanding Filipino verb tenses is essential for effective communication and fluency in the language.
Filipino verb tenses play a vital role in conveying actions within a specific context and allow speakers to communicate with precision.
Learning the variations in present, past, and future tenses sets the foundation for comprehending other tenses. The subtleties of aspect and mood in verb conjugation are crucial for nuanced expression of different situations and emotions in Filipino.
Understanding Filipino Verb Tenses
Understanding Filipino Verb Tenses is essential for effective communication and fluency in the language. Filipino verb tenses play a vital role in conveying actions within a specific context, making it crucial to understand their variations to choose the most contextually relevant form.
In Filipino, verbs are conjugated to indicate past, present, or future actions, allowing speakers to communicate with precision. To achieve this, it’s important to grasp the actor-focus and object-focus types of verbs and their corresponding affixes.
By focusing on verbs commonly used in daily conversations, learners can efficiently progress towards fluency. Learning to conjugate MAG and MA verbs, which are widely used in Filipino, can significantly contribute to your language proficiency.
Understanding these variations in Filipino verb tenses is a valuable aspect of language acquisition, providing a strong foundation for effective communication within the Filipino community.
Filipino Present Tense Variations
Present tense in Filipino verbs captures actions happening at the moment, adding depth to your understanding of Filipino verb tenses. When forming the present tense, Filipino verbs undergo variations by adding affixes to the verb root. These variations involve the use of prefixes, infixes, and suffixes, which are essential for conjugating Tagalog verbs accurately.
Understanding these present tense variations is crucial for effective communication, as they differ from English present tense aspects. By mastering the nuances of present tense variations, you can express actions happening at the moment with precision.
This knowledge also sets the foundation for comprehending different tenses, including verbs in the past, and contributes to your overall proficiency in using Filipino verb tenses.
Filipino Past Tense Variations
In Filipino, past tense verbs undergo variations by adding the prefix NAG- before the root verb to signify actions that occurred in the past. The prefix NAG- is used for actor-focus verbs in the past tense, while NAG- plus the first syllable of the root verb is used for specific conjugation patterns. For instance, ‘to study’ in the past tense is ‘nag-aral’, and ‘to watch’ is ‘nag-nood’. This distinction is particularly important when conjugating MAG verbs and UM verbs in the past tense. Filipino past tense verbs can be regular or irregular, and their conjugation follows specific patterns based on the verb type. Here’s an overview of the past tense variations:
| Verb Type | Example |
|---|---|
| MAG Verbs | nag-aral |
| UM Verbs | nag-nood |
| Irregular Verbs | nagbigay |
Filipino Future Tense Variations
Adding MAG at the beginning of the verb and repeating the first syllable of the root verb after MAG, followed by the full root verb, forms the future tense in Filipino. When dealing with MA verbs, use MA and the first syllable of the root verb for the future tense, while NA is used for the present and past tenses.
MAG verbs have future, basic, and imperative forms, whereas MA verbs are relatively straightforward in the future tense.
The present tense of MAG verbs is formed by replacing MAG with NAG, and the past tense is created by using NAG followed by the root verb.
Conjugating MAG verbs is relatively easy, as they’re actor-focus verbs in Filipino or Tagalog.
Subtleties of Aspect and Mood
Understanding the nuances of aspect and mood in Filipino verb conjugation is crucial for mastering the language, especially after delving into the variations of future tense with MAG and MA verbs.
In Filipino, verbs are conjugated to convey variations in aspect and mood, which are crucial for effective communication. The present, past, and future tenses are expressed not only through verb changes but also through the subtleties of aspect and mood.
These variations allow for a nuanced expression of different situations and emotions. Mastering these subtleties grants you the ability to communicate with precision and clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Different Tenses of Verbs in Filipino?
In Filipino, verb tenses express past, present, and future actions and states of being. Understanding the different tenses of verbs is essential for effective communication and fluency in Filipino.
How Do You Conjugate Filipino Verbs?
To conjugate Filipino verbs, you modify the root verb by adding prefixes, infixes, and suffixes to indicate tense and focus. MAG and MA verbs are commonly used, and their conjugation involves specific affixes for different tenses.
What Is the Verb Structure of Tagalog?
The verb structure of Tagalog involves using prefixes, infixes, and suffixes to indicate the tense of the verb. Understanding verb groups, such as MAG and MA verbs, is important for learning Tagalog verb conjugation.
Does Tagalog Have Future Tense?
Yes, Tagalog has a future tense. It’s formed by adding specific affixes or prefixes to the root verb. For actor-focus verbs, ‘mag-‘ or ‘mag-a’ is used, and for object-focus verbs, ‘ma-‘ or ‘ma-a’ is used.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the variations in Filipino verb tenses is essential for effective communication in the language.
Understanding the aspects of present, past, and future tense variations, as well as the subtleties of aspect and mood, is crucial for accurately expressing actions in Filipino.
By learning and practicing these variations, you can confidently navigate the complexities of Filipino verb conjugation and effectively convey your intended meaning in conversation.